Identify All of the Polyprotic Acids Below.
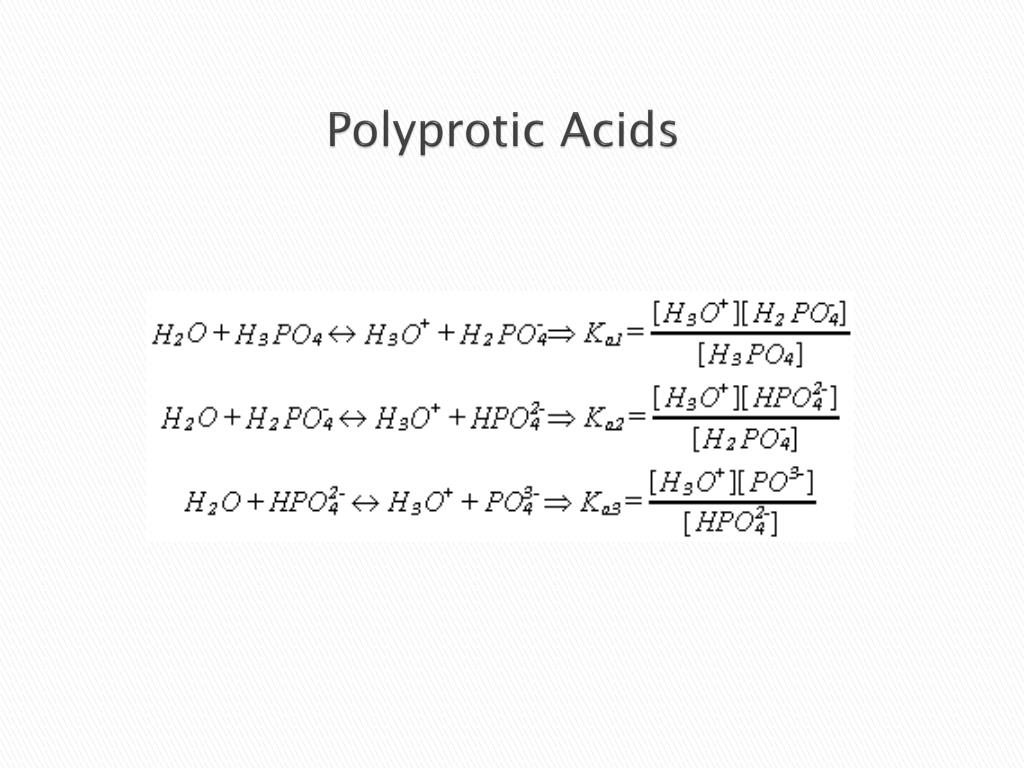
The titrant reacts with a solution of analyte. As you learned polyprotic acids such as H_2SO_4 H_3PO_4 and H_2CO_3 contain more than one ionizable proton and the protons are lost in a stepwise manner.
Ppt Polyprotic Acids Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 307396
Should be able to determine the three Ka values for citric acid and compare the result to the three known values given below.

. Pure water neutral 74. Given the titration curve of the hypothetical polyprotic acid X at 0100 M concentration pKa140 pKa280 pKa3120 titrated with 0600 M NaOH identify the. The acidity of acids is determined by the pKa of the acid.
Click to see the answer. The advantagesdisadvantages of titration depend on the situation and environment of testing however these are. Answer 1 of 3.
Explain why the introductory definition is a macroscopic definition while the Brønsted-Lowry definition and the Lewis. Identify the acid in the equation below and the base. In particular water itself can be.
A compound that donates a proton a hydrogen ion H to another compound is called a Brønsted-Lowry acid and a Lewis acid is any species that can accept a pair of electrons. Identify if an unknown acid is weak or strong and monoprotic or polyprotic. Calculate K a values of weak acids from titration data.
In the United States the labels traditionally were numerals with capital letters. In the laboratory hydrogen chloride HClg and ammonia NH 3 g often escape from bottles of their solutions and react to form the ammonium chloride NH 4 Cls the white glaze often seen on glasswareAssuming that the number of moles of each gas that escapes into the room is the same what is the maximum partial pressure of HCl and NH 3 in the laboratory at room. Calculate initial concentrations of monoprotic acids from titration data.
Ka is the acid dissociation constant of a solution. Diprotic and polyprotic acids show unique profiles in titration experiments where a pH. PKa is the negative logarithm of Ka.
Expansion of Gases Let say you are tasked to do the following where you 1. HCl NH3 NH4 Cl-Unlike the Arrhenius definition the Bronsted-Lowry definition does not involve water so this definition is a little more universal than the Arrhenius definition. Sodium hydroxide Not All Liquids Have a pH Value.
We work with many acids low pH and bases high pH every day. Write the condensed noble-gas electron configuration of. PH only has meaning in an aqueous solution in water.
The terminus of the liquid-gas curve represents the substances critical point the pressure and. Complete the following nuclear equations and identify X in each case A. However IUPAC recommends that the numbers 1 through 18 be used and these labels are more common.
Acids can also be categorized as monoprotic acids and polyprotic acids. When the unknown solution is a weak acid or base the. H 3 C 6 H 5 O 7 aq H 2 Ol H 2 C 6 H 7 O 7- H 3 O K a1 74x10-3 25 o C H 2 C 6 H 5 O 7- H 2 Ol HC 6 H 6 O 7 2-.
This information can be used to help identify the acid in question since Ka for a large number of polyprotic acids are known. For the table to fit on a single page parts of two of the rows a total of 14 columns are usually written below the main body of the table. Titration also known as titrimetry and volumetric analysis is a common laboratory method of quantitative chemical analysis to determine the concentration of an identified analyte a substance to be analyzed.
At pressures below the triple point a substance cannot exist in the liquid state regardless of its temperature. Two common examples are carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 which has two acidic protons and is therefore a diprotic acid and phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 which has three acidic protons and is therefore a triprotic acid. Titration is a technique where a known concentration of solute is used to find the concentration of an unknown solution.
As their name suggests polyprotic acids contain more than one acidic proton. The fully protonated species is always the strongest acid because it is easier to remove a proton from a neutral molecule than from a negatively charged ion. Attach a small rubber A.
DISCUSSION Titration is a technique used in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of an unknown solution. The point of intersection of all three curves represents the substances triple pointthe temperature and pressure at which all three phases are in equilibrium. A reagent termed the titrant or titrator is prepared as a standard solution of known concentration and volume.
Monoprotic acids release one hydrogen ion per molecule whereas polyprotic acids release more hydrogen ions per molecule. A question based on properties of gases that is to be accomplished. The flat region of the curve is the buffer region because moving along the x-axis adding an acid or base has the smallest change along the Y axis Delta pH and the titration curves for all of the acids and bases in figure 1735 are flattest at half titer.
Examples of pH values of lab chemicals and household products include. In the chapter on acids and bases we saw two more definitions of acids. However as noted earlier many Arrhenius acids and bases can be considered Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases as well.

Polyprotic Acid Base Equilibria Problems Ph Calculations Given Ka1 Ka2 Ka3 Ice Tables Youtube

Weak Acids Ka P Ka Polyprotic Acids Warning
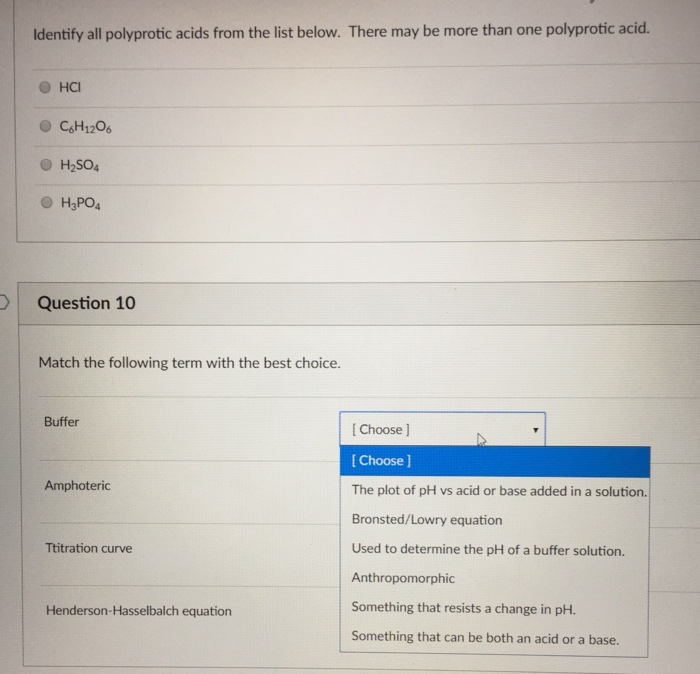
Solved Identify All Polyprotic Acids From The List Below Chegg Com

Solved Polyprotic Acids A Polyprotic Acid Has More Than One Chegg Com

Comments
Post a Comment